Topics
PLC, product life cycle, marketing models, strategy, marketing mix
Review the activity below or download the PDF student worksheet
- Student Worksheet: Understanding the Product Life Cycle (PLC)
- Instructor Solutions (Members Only): Understanding the Product Life Cycle (PLC)= Solutions
Student Discussion Activity
Introduction
We all should know the product life cycle (PLC) model and its four stages of:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Some textbooks also include a fifth stage, which is BEFORE the new product comes to market – usually labelled the product development stage. But for this activity we are primarily concerned with the four stages listed above – which are all AFTER a product comes to market.
Your Task
In this activity, your task is to complete the following two tables. These are tables that we will see in marketing textbooks, but because it has a lot of boxes, we often only give it a quick glance and don’t get into the detail and we miss a lot – well, here’s our chance to dig in deeper and better understand this key marketing model.
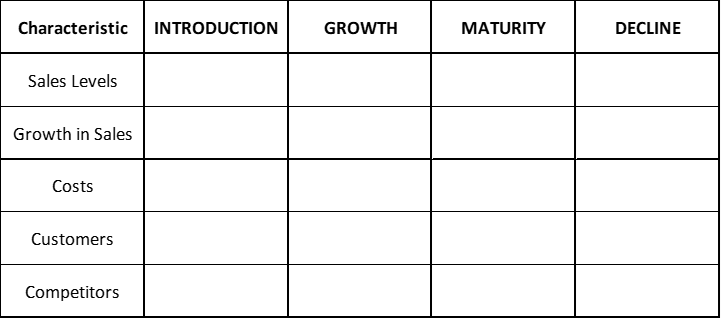
TABLE 1 = Key Characteristics of Each PLC Stage
Please complete the table by inserting the terms listed underneath – note that each term is only used once – you can simply write the number in the right box.
- Medium, but declining, sales levels
- High costs per customer/sale
- Mostly early adopters
- Moderate growth in sales
- A decreasing number of competitors
- An increasing number of competitors
- Mostly innovators
- Negative growth in sales levels
- Low, but unstable, costs per customer/sale
- High and stable sales levels
- High, but reducing, costs per customer/sale
- Low sales levels
- Initially no competitors, but then a few more
- Sales growth in line with overall economic growth
- Mostly laggards
- Low and reducing costs per customer/sale
- Mixed sales levels (medium to high)
- Numbers of competitors are relatively stable
- A mix of the early and late majority
- Rapid growth in sales levels
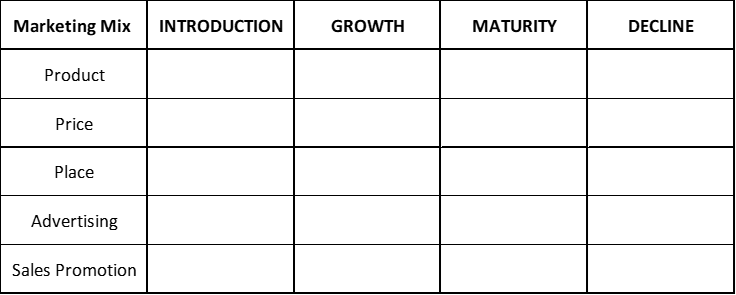
TABLE 2 = Key Marketing Mix Tactics for Each PLC Stage
Please complete the table by inserting the terms listed underneath – note that each term is only used once – you can simply write the number in the right box.
- Build intensive distribution
- Utilize sales promotions to generate consumer trials
- Progressively phase out poorer selling product lines
- Increase product differentiation and augmentation
- Build selective distribution
- Price to maximize profits as sales decline
- Use price skimming or penetration depending upon latent demand
- Utilize sales promotion to encourage brand switching
- Promote the brand’s positioning and competitive advantages
- Create awareness among innovators and suitable channels
- Expand product line extensions
- Offer a single or basic product only
- Use penetration pricing to gain market share
- Utilize sales promotions to win market share
- Reduce distribution channels
- Promote to early adopters and the early majority
- Use competitive pricing
- Maximize intensive distribution
- Minimize promotional spend on advertising
- Utilize sales promotions to retain interest in the product
Related Activities